You are here:iutback shop > price
Calculate ARIMA 1 1 1 for Bitcoin Price: A Comprehensive Guide
iutback shop2024-09-21 19:29:03【price】7people have watched
Introductioncrypto,coin,price,block,usd,today trading view,IntroductionBitcoin, the world's first decentralized digital currency, has been a topic of interest airdrop,dex,cex,markets,trade value chart,buy,IntroductionBitcoin, the world's first decentralized digital currency, has been a topic of interest
Introduction
Bitcoin, the world's first decentralized digital currency, has been a topic of interest for investors and researchers alike. Its price volatility has made it a challenging asset to predict. One of the most popular time series forecasting methods is the ARIMA (AutoRegressive Integrated Moving Average) model. In this article, we will discuss how to calculate ARIMA 1 1 1 for Bitcoin price, providing a comprehensive guide to help you understand the process and its implications.
What is ARIMA?
ARIMA is a forecasting method that uses historical data to predict future values. It is a combination of three components: Autoregression (AR), Moving Average (MA), and Differencing. The ARIMA model is represented as ARIMA(p, d, q), where p is the number of lag observations included in the model, d is the number of times that the raw observations are differenced, and q is the size of the moving average window.
In this article, we will focus on the ARIMA(1, 1, 1) model, which is a popular choice for Bitcoin price forecasting. The ARIMA(1, 1, 1) model suggests that the current value of Bitcoin is influenced by the previous value and the difference between the current and previous values, as well as the difference between the current value and the average of the previous q values.
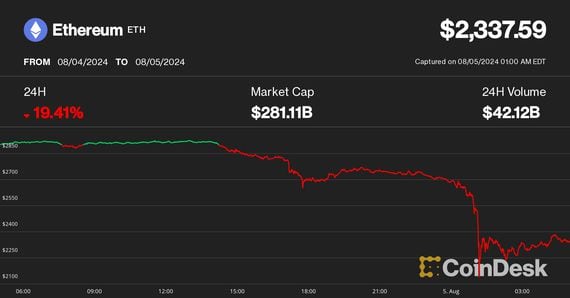
Calculating ARIMA 1 1 1 for Bitcoin Price
To calculate ARIMA 1 1 1 for Bitcoin price, follow these steps:
1. Collect historical Bitcoin price data: Obtain a dataset containing historical Bitcoin prices, such as closing prices or average prices. Ensure that the data is in a time series format, with dates or time stamps.
2. Plot the data: Visualize the Bitcoin price data using a line chart to identify any trends, seasonality, or cycles.
3. Check for stationarity: ARIMA models require stationary data. If the data is non-stationary, apply differencing to make it stationary. In our case, we will use first-order differencing (d=1) to transform the data.

4. Identify the ARIMA parameters: Use statistical tests, such as the Autocorrelation Function (ACF) and Partial Autocorrelation Function (PACF), to determine the values of p and q. For the ARIMA(1, 1, 1) model, p=1, d=1, and q=1.
5. Fit the ARIMA model: Use a statistical software or programming language, such as Python with the statsmodels library, to fit the ARIMA(1, 1, 1) model to the data.
6. Evaluate the model: Assess the accuracy of the ARIMA model by comparing the forecasted values with the actual values. Calculate metrics such as Mean Absolute Error (MAE) or Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) to measure the model's performance.
7. Forecast future Bitcoin prices: Once the ARIMA model is deemed accurate, use it to forecast future Bitcoin prices. The model will predict the next value based on the previous value and the difference between the current and previous values.

Conclusion
Calculating ARIMA 1 1 1 for Bitcoin price involves several steps, including data collection, plotting, checking for stationarity, identifying parameters, fitting the model, evaluating its accuracy, and forecasting future prices. By following this comprehensive guide, you can gain insights into the Bitcoin price dynamics and make informed decisions based on the ARIMA model's predictions. However, it is important to note that forecasting financial markets is inherently uncertain, and the ARIMA model should be used as a tool to support decision-making rather than a definitive predictor of future prices.
This article address:https://www.iutback.com/eth/13f42099566.html
Like!(826)
Related Posts
- The Rise of $100 Bitcoin on Cash App: A Game-Changer for Cryptocurrency Users
- Bitcoin Mining Austin TX: A Thriving Industry in the Heart of Texas
- Bitcoin Mining Mineral Oil: A Sustainable Solution for Energy Consumption
- How to Send Crypto to Metamask from Binance: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Live Bitcoin Price Quotes: The Ultimate Guide to Tracking Cryptocurrency Value
- Binance FTM BTC: A Comprehensive Guide to Trading and Investing
- Zombie Bitcoin Wallet List: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Navigating the Cryptocurrency Landscape
- Title: Navigating the Insufficient Gas Binance Wallet Issue: A Comprehensive Guide
- Unlocking the World of Free Bitcoin Cash Games: A Gamers' Paradise
- **The Regulatory Landscape of Look SEC, Coinbase, and Binance
Popular
Recent

How Do I Find My List Bitcoin Wallet Address Lookup: A Comprehensive Guide
Bitcoin Wallet for Computer: The Ultimate Guide to Secure Digital Currency Storage

Bitcoin Wallet for Computer: The Ultimate Guide to Secure Digital Currency Storage

Import Private Key in Bitcoin ABC Wallet: A Comprehensive Guide

Bitcoin Mining Software for PC: A Comprehensive Guide

Bitcoin Private Price Prediction: A Reddit Community's Insight

What Was the Bitcoin Price in 2009?

Bitcoin Wallet for Computer: The Ultimate Guide to Secure Digital Currency Storage
links
- Dec 2016 Bitcoin Price: A Look Back at the Cryptocurrency's Milestone
- How Does OTC Desk Transfer Bitcoins into Cash?
- Best Bitcoin Wallet for a New User: A Comprehensive Guide
- Where Can You Buy Bitcoin for Cash?
- Bitcoin Price Calculator Date: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Bitcoin's Value Over Time
- The Bitcoin Cash Volatility Index: A Comprehensive Analysis
- Is Binance Still Trading XRP?
- The Price of Bitcoin by the End of 2021: A Comprehensive Analysis
- Stake Bitcoin Cash: A Comprehensive Guide to Earning Passive Income
- How Do I Check If I Have Bitcoin Cash?